DATA COMMUNICATIONS
• This
course provides a broad introduction to the fundamentals of data communications
and network technology. It teaches the users basic networking concepts and
skills. It also provides an understanding of data communication standards.
Further, it provides an overview of how data is transferred in a real-world
network environment
Static vs. Dynamic Web
Application
Ø Text
Books: Stallings, W. (2007) Data and Computer Communications, 8th
education. Pearson Education International.
Ø Reference
Books: Leon-Garcia, A and Widjaja, I (2004) Communica8on Networks: Fundamental
Concepts and Key
How to access the Web?
• Once
you have your Internet connection, then you need special software called a browser to access the Web
• Browser : is a special program
used to locate, retrieve and display content on the www including Web pages,
images, video and other files
Client/Server Structure
of the Web
• Web
is a collection of files that reside on computers, called Web servers,
• Web
servers are located all over the world and are connected to each other
through the Internet
• When
you use your Internet connection to become part of the Web, your computer
becomes a Web client in a
worldwide client/server network
• A
Web browser runs on your
computer to make it work as a web client
Web-based systems
architectures
•
Browser(client)
requests for a particular web page(HTML file)
•
The sever
locates the file and send it to the browser
•
The
browser(client) display the file
Introduction to Networks
DATA
COMMUNICATIONS
•
The term telecommunication
means communication at a distance
•
The word data
refers to information presented in whatever form is agreed upon by the parties
creating and using the data
•
Data
communications are the exchange of data between two devices via some form of transmission
medium such as a wire cable
Data
communication system components
Five components of data communication
•
Message
–
Is the information(data) to be communicated.
–
(text, numbers, pictures, sound, video
or any combination of these)
•
Sender
–
Is the device that sends the data message.
–
(computer, workstation, telephone
handset, video camera)
•
Receiver
–
Is the device that receives the message.
–
(computer, workstation, telephone
handset, video camera)
•
Medium
–
Is the physically path by which a message
travels from sender to receiver.
–
(twisted pair wire, coaxial cable,
fiber- optic cable, laser , or radio waves(terrestrial or satellite microwave))
•
Protocol
Is a set of rules that govern data
communication
Direction of Data Flow
•
Is used to
define the direction of signal flow between two link devices
ü Unidirectional, as on a one-way street (keyboard,
monitor)
•
Half-Duplex
ü Each station can both transmit and receive, but not
at the same time
•
Full-Duplex
ü Both stations can transmit and receive
simultaneously
WHAT IS COMPUTER
NETWORKS
•
A network is a
set of devices (often referred to as nodes) connected by communication links in
order to communicate and share resources.
•
A node can be
a computer, printer, or any other device capable of sending and/or receiving
data generated by other nodes on the network.
•
Computers may
connect to each other by either wired or wireless media.
Classification of Computer Networks
Computer networks are classified based on various factors. They includes:
•
Geographical
span
•
Inter-connectivity(topology)
•
Connection
Method
•
Architecture
Geographical span
•
Computer
networks may be classified according to the scale
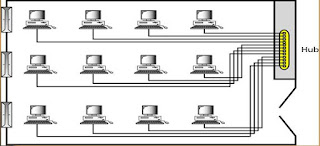
ü Local area network (LAN)
ü Metropolitan area network (MAN)
ü Wide area network (WAN)
•
LAN connects
networking devices with in short span of area, i.e. small offices, home,
internet cafes etc
•
spanned inside
a building and operated under single administrative system
•
It uses TCP/IP
network protocol for communication between computers
•
LAN provides a
useful way of sharing the resources between end users. The resources such as
printers, file servers, scanners, and internet are easily sharable among
computers
•
LAN can be
wired,wireless, or in both forms at once.
Geographical span- Metropolitan Area Network(MAN)
•
MAN generally
expands throughout a city such as cable TV network
•
Metro Ethernet
is a service which is provided by ISPs
•
This service
enables its users to expand their Local Area Networks.
•
For example,
MAN can help an organization to connect all of its offices in a city.
•
MAN works in
between Local Area Network and Wide Area Network
•
MAN provides
uplink for LANs to WANs or internet
Geographical span- Wide Area Network (WAN)
•
WAN connection
between computers over large geographical areas that may comprise a country, a
continent, or even the whole world
•
Dedicated
transoceanic cabling or satellite uplinks may be used to connect this type of
global network
•
These networks
provide connectivity to MANs and LANs
By network topology
•
Network
topology is the arrangement of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.)
of a computer network
•
Topologies may
define both physical and logical aspect of the network
•
There are
several common physical topologies
•
Star Network
•
Ring Network
•
Mesh Network
•
Star-Bus
Network
Tree or Hierarchical Topology Network
Network Architecture
•
Computer
networks may be classified according to the functional relationships which
exist between the elements of the network
•
There are two
type of network architecture :
ü Client-Server
ü Peer-to-Peer Architecture
By Connection Method
•
Computer
networks can also be classified according to the hardware technology that is used
to connect the individual devices in the network such as Optical fibre,
Ethernet, Wireless LAN.






No comments:
Post a Comment